

Freshwater, for example, comes mostly from desalination plants in some countries because of its scarcity from natural sources. Knowledge of the thermodynamic properties of electrolyte solutions is relevant for the design of many classes of chemical processes (Chen, 2006), some of which of very large scale. Keywords: Thermodynamics Equilibrium Aqueous solutions Solubility Precipitation. The procedure has proven to be reliable and fast and the results are in good agreement with literature data.

PREDICTING PRECIPITATE FREE
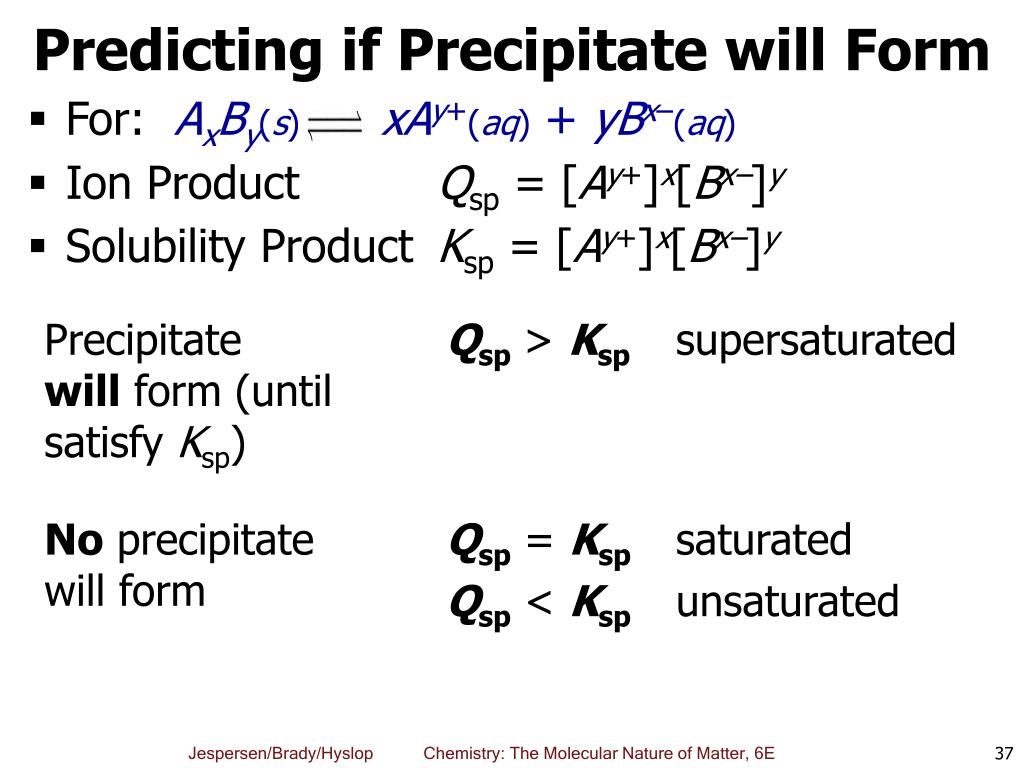
It is possible to use the procedure with several excess Gibbs free energy models for liquid phase behavior. The criteria used for phase stability may lead, in some cases, to the premature inclusion of phases that should be absent from the final solution but, if this happens, the phase elimination sub-procedure removes them. After the phase splitting calculation for a system configuration that has a certain number of phases, the phase stability test establishes whether including an additional phase will reduce the Gibbs free energy further. The procedure combines three sub-procedures: phase stability test, minimization of the Gibbs free energy with a stoichiometric formulation of the salt-forming reactions to compute phase splitting, and a phase elimination test. E-mail: article proposes a new procedure to compute solid-liquid equilibrium in electrolyte systems that may form pure solid phases at a given temperature, pressure, and global composition. IIIDepartment of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering, U.A.E. IIInstituto de Química, Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro - RJ, Brazil IBuckman Laboratories, Campinas - SP, Brazil This work was partially done at COPPE/UFRJ. On leave from Escola de Química, Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro. To whom correspondence should be addressed Thermodynamics Equilibrium Aqueous solutions Solubility PrecipitationĪ reliable procedure to predict salt precipitation in pure phases

This article proposes a new procedure to compute solid-liquid equilibrium in electrolyte systems that may form pure solid phases at a given temperature, pressure, and global composition.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
